Key Differences Between eCommerce For B2B and B2C
Businesses of all types are adapting to new ways of reaching customers and clients, as reliance on their typical channels generate lower profits. Two major categories in the eCommerce landscape are Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Consumer (B2C) eCommerce. While both involve equipping businesses for selling their products online, each has their own key factors that define success. In this article, we’ll explore the key variations between B2B and B2C eCommerce, highlighting their unique characteristics and the implications for businesses operating within each sphere.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Target Audience and Customer Base
- Purchase Decision Complexity
- Sales Process and Relationship Building
- Product Catalog and Customization
- Pricing Structure
- Marketing and Branding Strategies
- User Experience and Website Design
- Payment and Checkout Processes
- Customer Support and After-Sales Services
- Mobile Responsiveness
- Data Privacy and Security
- Regulation and Compliance
- Analytics and Metrics
- Conclusion
Introduction
B2B e-commerce, or business-to-business e-commerce, refers to the online transaction of goods and services between businesses. Unlike B2C e-commerce, where businesses sell directly to consumers, B2B e-commerce involves transactions between one business entity and another. This model often involves larger order quantities, complex pricing structures, and negotiations tailored to the specific needs of each business.
Key Features and Benefits of B2B E-commerce
- Personalized Pricing and Negotiation: B2B e-commerce platforms offer the flexibility to provide customized pricing based on factors such as order volume, recurring purchases, and customer loyalty. This personalized approach fosters stronger business relationships.
- Streamlined Procurement: B2B e-commerce streamlines the procurement process by allowing businesses to place orders online, track shipments, and manage inventory. This efficiency translates to time and cost savings.
- Bulk Ordering: B2B transactions frequently involve bulk orders. E-commerce platforms designed for B2B transactions make it seamless for businesses to place large orders and manage inventory efficiently.
B2C e-commerce, or business-to-consumer e-commerce, is the model most individuals are familiar with. It involves transactions where businesses directly sell products or services to individual consumers. B2C e-commerce platforms are designed to deliver a user-friendly and personalized shopping experience.
Noteworthy Attributes and Advantages of B2C E-commerce
- Mass Market Appeal: B2C e-commerce caters to a wider audience, often with smaller individual order sizes. This approach capitalizes on high transaction volumes and broad brand visibility.
- Emphasis on User Experience: B2C e-commerce platforms prioritize user experience, offering intuitive navigation, personalized recommendations, and easy checkout processes. A seamless shopping experience leads to higher conversion rates.
- Brand Loyalty and Engagement: Successful B2C e-commerce strategies focus on building brand loyalty through engaging content, targeted marketing campaigns, and exceptional customer service.
Target Audience and Customer Base
B2B eCommerce primarily caters to businesses and professionals. The target audience includes wholesalers, manufacturers, suppliers, and other entities that require bulk purchases. In contrast, B2C eCommerce focuses on individual consumers seeking retail products for personal use. Naturally, this means that B2C will have the larger audience and require much less precision in targeting, and can cast a wider net with less emphasis on specialization.
- B2B Strategies: Focus on building strong relationships with clients, offering customized solutions, and utilizing data-driven insights to refine pricing and offerings.
- B2C Strategies: Prioritize user experience, invest in digital marketing, and utilize social media platforms to engage and retain customers.
Purchase Decision Complexity
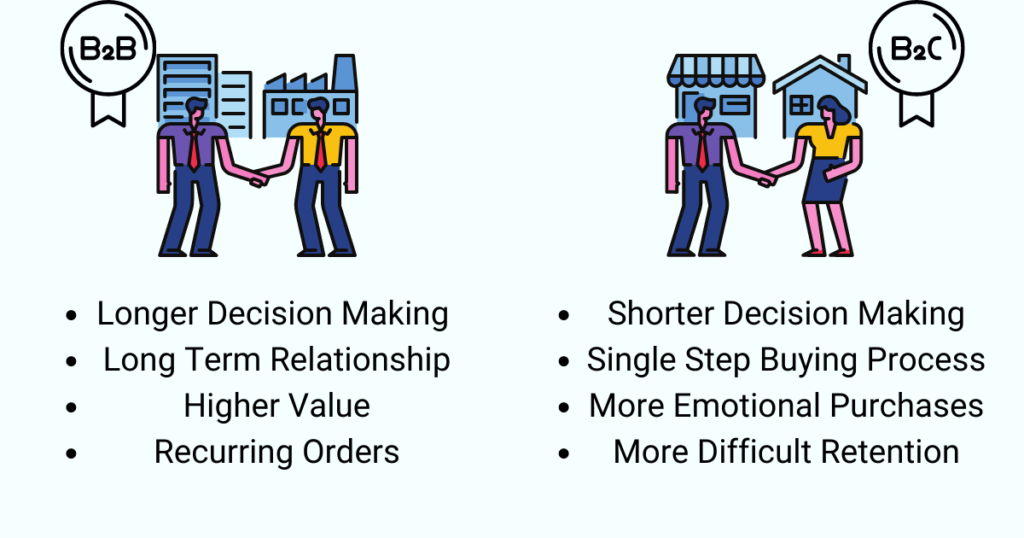
B2B transactions often involve complex decision-making processes. Purchases are typically based on factors such as budget considerations, long-term contracts, and the alignment of products with business goals. B2C purchases, on the other hand, are often driven by personal preferences, emotions, and immediate needs.
Sales Process and Relationship Building
B2B sales cycles are generally longer and involve building strong relationships with clients. B2B businesses emphasize personalized communication, negotiations, and addressing specific business needs. B2C transactions tend to be more transactional, with a focus on creating a seamless and convenient shopping experience.
Product Catalog and Customization
B2B eCommerce platforms offer extensive product catalogs tailored to the needs of business customers. Customization options are crucial to meeting specific requirements, or saving potential buyers time by using filters to only target the products of interest to them. B2B buyers are much less likely to spend time idly browsing and need features that will condense decision making factors as directly as possible. In B2C, the emphasis is on showcasing a wide range of products appealing to individual consumer preferences and hoping that some resonate on an emotional level.
Pricing Structure
B2B pricing structures often involve negotiated contracts, bulk discounts, and tiered pricing based on order volume. B2C pricing is usually fixed for individual products, with occasional discounts or promotions. To assist with the more responsive and dynamic targeting our B2B users would be relying on, our software utilizes features such as price lists, that can alter pricing for any number of products and assigned to groups of various customers, and coupon codes, which can be generated based on percentages or fixed amounts, then distributed promotionally to users at the admins’ discretion.
Marketing and Branding Strategies
B2B marketing relies on targeted campaigns, industry partnerships, and educational content to attract businesses. B2C marketing focuses on emotional appeals, lifestyle branding, and creating a connection with individual consumers.
User Experience and Website Design
B2B eCommerce platforms prioritize functionality and efficiency, with an emphasis on facilitating complex transactions. B2C websites emphasize intuitive navigation, visually appealing design, and a seamless checkout process.
Payment and Checkout Processes
B2B payments often involve invoice-based transactions and credit terms. B2C transactions mostly occur through immediate online payments. One of the biggest disadvantages with some of the larger, more traditional B2B eCommerce software software tends to be transaction fees attached to orders, which depending on the users’ product value, can end up consuming a sizable amount of profit. Our policy at inSitu Sales is to ensure software options for distributors of every size, and as such, our payment processing gateways offer integration at no added cost.
Customer Support and After-Sales Services
B2B customer support involves dedicated account management and personalized assistance. B2C customer support is geared toward resolving individual concerns and providing a positive post-purchase experience.
Mobile Responsiveness
Both B2B and B2C eCommerce need to be mobile-responsive, but the specific requirements can differ based on user behavior and preferences.
Data Privacy and Security
B2B transactions may involve sensitive business data, necessitating stringent security measures. B2C transactions focus on safeguarding customer information.
Regulation and Compliance
B2B transactions often require adherence to industry-specific regulations. B2C transactions are subject to broader consumer protection regulations.
Analytics and Metrics
B2B eCommerce measures success through metrics like customer lifetime value and lead generation. B2C eCommerce focuses on metrics like conversion rates and customer acquisition costs.
Conclusion
In the dynamic world of eCommerce, understanding the nuances between B2B and B2C models is essential for crafting successful digital strategies. Each model caters to distinct audiences, necessitating tailored approaches to marketing, sales, and customer engagement.
Remember, success lies in aligning your e-commerce strategy with your unique business goals and target audience. Take charge of your e-commerce journey today, and propel your business towards digital success.
